In a small company, which does not have the resources for an advanced infrastructure and can only have an On-Premise installation, it is possible to obtain a good architecture within the limitations offered by the resources available to obtain a good implementation.
WHY DID I DECIDE TO RESTRUCTURE THE SERVICES?
At first, I ran into an inefficient service organization. What led me to make changes was:
- A VM with a MULTIPURPOSE CENTRAL SERVER that offered DC/AD, DNS, DHCP, FILE SHARING, SQL SERVER, ERP, APPS services. Everything on the same Windows Server installation. This can be very economical or take advantage of the resources within the same VM in a dynamic way due to Windows resource management, but these services were not independent from each other, so if any failed, in the worst case, the server had to be restarted, interrupting the rest of the services that had no problem.
- This server had an outdated version of Windows Server, resulting in security and functionality issues.
- There was also another file server in a separate VM, implemented in Linux and for this reason it was not regulated in AD.
- The network security configuration was applied by the pfsense solution with a VM, which did not offer the granularity and functionality necessary for the company.
- In addition, there were other VMs with specific applications that were wasting virtualized resources since most of them used one VM per service.
For these reasons, it was decided to migrate to a more complex and robust architecture that does not waste so many resources, as well as offering a more granular separation of services.
It is worth mentioning that all the changes were made according to the resources I had available.
OBJECTIVES
Then, the objectives to be met to solve these inconveniences are listed:
- INDEPENDENCE OF OPERATION: The services must be able to be managed independently so any situation does not affect the other services
- GOOD AVAILABILITY: The services must be supported with some redundancy, in order to offer a service with the highest possible availability.
- RESOURCE OPTIMIZATION: Services should consume only the resources they need and release the rest so that they are available to other services.
- DATA INTEGRITY: The greatest possible integrity must be safeguarded, so in its design there must be a good backup solution, both in technology and strategy.
TASKS
To achieve these objectives, the following activities are carried out:
- RESTRUCTURING OF PHYSICAL SERVERS (for Resource Optimization)
- SERVICE ISOLATION (for Independence of operation)
- REPLICAS OF VMs (for Good Availability)
- CREATION of VM and DOCKER SERVERS (for Resource Optimization)
- CREATION OF BACKUP SERVERS (for Data integrity)
RESTRUCTURING OF PHYSICAL SERVERS
There are 3 small physical servers of different technologies. These servers are not new or powerful, but since it is the only existing hardware, they are modified to obtain the maximum performance from them:
- HP PROLIANT ML150 G3 (2 logical cores, 4GB RAM)
- This is the worst equipped server, so I decided not to virtualize it and instead install a Windows Server with a single application (VEEAM B&R) to work as a BACKUP server
- HP PROLIANT DL160 G10 (6 logical cores, 32GB RAM)
- This is the newest server available, but poorly sized. Will be used with VMWARE ESXI virtualization as SRV1
- IBM SYSTEM X3550 M4 (12 logical cores, 32GB RAM)
- This server, on the other hand, is better equipped, but it has been in use for a few years. Will be used with VMWARE ESXI virtualization as SRV1
The last two servers will be used as replication mirrors. This is described below.
SERVICE ISOLATION
In order to choose which devices offer certain services and to obtain a better isolation of them, they were grouped according to the CIA concept (Confidentiality, Integrity and Availability) and separated according the convenience as follows:
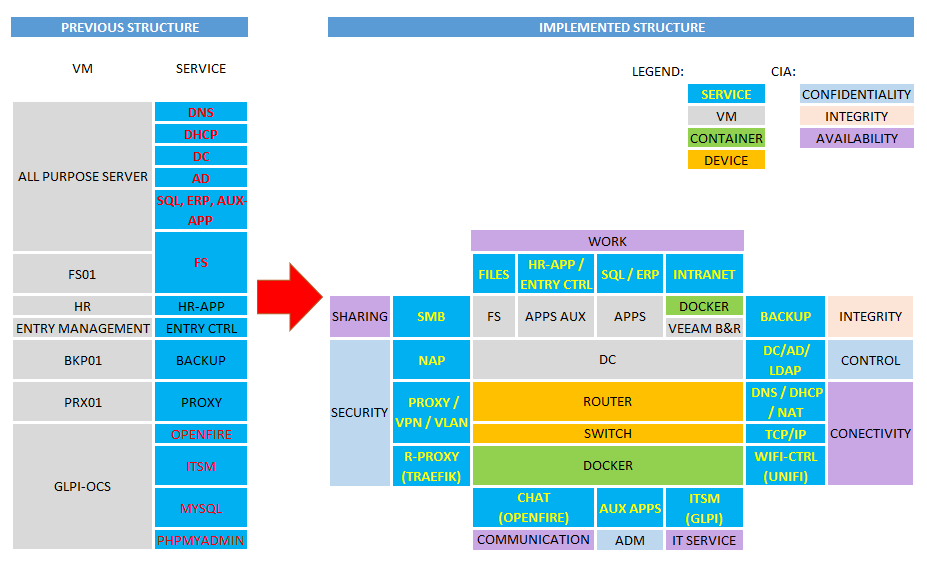 The figure shows the isolation of services before and after.
The figure shows the isolation of services before and after.
Therefore, in terms of:
CONFIDENTIALITY: The following services are configured to offer security and protection of information as follows:
- ROUTING, PROXY, VPN, VLAN: physical devices such as Router and Switches were used, due to their capacity, speed and convenience
- NAP, AD, DC, LDAP: for these services Windows Server is deployed in a VM due to its association with the Microsoft environment.
- Reverse-PROXY: is implemented with TRAEFIK through DOCKER due to its ease of use and allows to protect internal services through SSL certificates.
INTEGRITY: the following services were provided to offer protection in terms of backing up information in case of loss, as follows:
- BACKUP: VEEAM B&R and DOCKER were used.
- VEEAM takes care of the backups of VMs, physical machines and folders. The backup is deposited on disks according to an Online/Offline Backup schedule and strategy.
- DOCKER is in charge of backups through DUPLICATI with backup in the cloud for the data of the services deployed in DOCKER
AVAILABILITY: The following services were provided in terms of:
- CONNECTIVITY:
- DNS, DHCP, NAT: a physical device was used as a Router for its capacity, speed and convenience.
- TRANSPORT: physical device such as Switch was used for its capacity, speed and convenience.
- WIFI-CONTROLLER: a UNIFI DOCKER container was used due to the need to use resources and convenience.
- REDUNDANCY:
- ISP FAILOVER: a physical device was used as a Router for the FAILOVER service with two ISPs to offer REDUNDANCY of service, due to its capacity, speed and convenience.
- VM REPLICAS: VEEAM replicates VMs between physical servers to obtain a kind of non-automatic FAILOVER, which allows VMs to be set up in a short time and to obtain good availability despite the few available resources.
- DOCKER SWARM: this technology is used to offer uninterrupted container service. This is already available in DOCKER and offers a good service.
- COMMUNICATION:
- The CHAT service is implemented with OPENFIRE for internal communications through DOCKER.
- IT SERVICE:
- The ITSM service is implemented with GLPI for the management of ASSET MANAGEMENT, HELP and SERVICE DESK also through DOCKER.
- SHARING:
- The SMB FILE SHARING service is implemented on a Windows Server VM for its convenience of functionality and compatibility with the Microsoft environment.
- WORK SERVICES: the following services are described:
- REMOTE APP: it is implemented in a VM with Windows Server, given its nature and needs of the different departments of the company.
- SQL, ERP: it is implemented in a VM with Windows Server, given its nature and needs of the different departments of the company.
- INTRANET: it is implemented in DOCKER and consists of a Web server with the development of a page that offers required services.
More about specific steps I did to ensure data integrity and good availability, please read here.
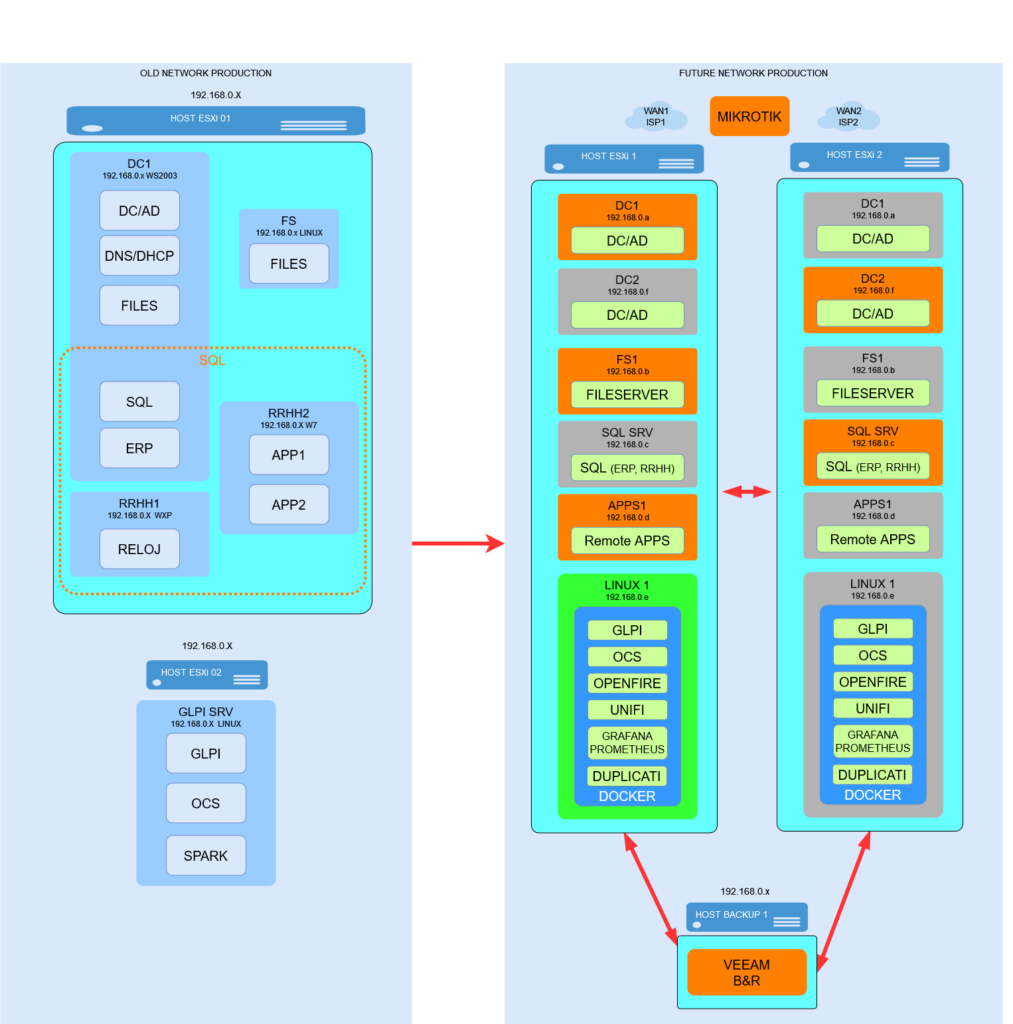
REPLICAS OF VMs
Through the Backup server, replicas of VMs are made to obtain a mirror on each server, thus being able to opt for the mirror replica in case of failure of one. This is possible with the use of VEEAM B&R
- The services was grouped according to their type and distributed on different devices to obtain the best independence of operation:
The figure shows the change from a precarious structure (on the left) to a structure (right) with the advantages mentioned above.
The distribution of the active VMs (in orange) and those that are turned off (in gray) is shown. These are replicas of the active ones and are arranged so that if a failure occurs, they can be manually activated. It doesn’t offer uninterrupted service or failover, but at least downtime is as short as possible.An attempt has been made to separate the services as best as possible given that there were only 2 servers with the capacity for virtualization and a low-resource server (Veeam B&R) to make backup copies and replicate the virtual machines.
CREATION OF DOCKER SERVERS
A VM with Linux and Docker for container management is created to create the services that cover:
- COMMUNICATION
- DOCKER ADMINISTRATION
- IT SERVICES
- INTRANET
- BACKUP
LIMITATIONS:
- This structure does not offer FAILOVER for the VMs, but as described, it only has replicas that can be activated when necessary. This allows for as little downtime as possible.
- This structure does not have a DR system, meaning that if a disaster occurs it can only offer replacement of backup VMs, this implies that the last operating state of the copies will be obtained depending on:
- Time when the last SNAPSHOT was obtained
- The severity of the disaster
- The frequency of exchanging copies Offline
Consequently, as much information as possible can be recovered in the event of a disaster. In addition, the time to restore the operation of the systems is defined by the recovery time of the backups and the eventual adjustments that must be made in the environment of services and clients.
- This structure does not have redundancy of the physical devices, due to the low budget that the company manages. This can lead to some downtime in case of breakage and depending on the device in question, it will be the duration of this time.